The Role of a Cloud Architect in Modern Technology
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the demand for efficient and scalable cloud solutions is higher than ever. Companies of all sizes are migrating their operations to the cloud to harness its benefits. But who ensures that these cloud infrastructures are well-designed, secure, and perform optimally? That's where a Cloud Architect steps in.
What is a Cloud Architect?
A Cloud Architect is a professional responsible for designing, planning, and overseeing an organization's cloud infrastructure. They are the architects of the digital realm, ensuring that cloud systems meet a company's needs while optimizing costs and resources.
Defining Cloud Computing
To understand the role of a Cloud Architect, we must first grasp the fundamentals of cloud computing. Cloud computing involves delivering computing services, including storage, databases, networking, software, and more, over the internet. It eliminates the need for physical hardware and provides on-demand, scalable resources.
Types of Cloud Computing Models
There are three primary cloud computing models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications via the web.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers several advantages, including cost-efficiency, scalability, and accessibility. It allows businesses to adapt to changing demands and reduces the burden of maintaining physical infrastructure.
The Role of a Cloud Architect
Cloud Architects play a vital role in making cloud computing work for organizations. They must possess a unique set of skills and knowledge to fulfill their responsibilities.
Responsibilities and Skills
- Designing Cloud Solutions: Cloud Architects create the blueprint for cloud infrastructure, considering factors like performance, security, and cost.
- Collaboration with IT Teams: They work closely with IT teams to ensure seamless integration and maintenance of cloud solutions.
- Staying Updated with Cloud Technologies: The tech world evolves rapidly, and Cloud Architects must keep up with the latest advancements in cloud computing.
Designing Cloud Solutions
A significant part of a Cloud Architect's role is designing solutions that align with an organization's needs. This entails:
- Architectural Considerations: Deciding between public, private, or hybrid cloud models.
- Security and Compliance: Ensuring data security and regulatory compliance.
- Scalability and Performance: Designing for growth and optimizing performance.
Cloud Service Providers
When selecting a cloud service provider, organizations have multiple options, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Major providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Becoming a Cloud Architect
If you aspire to become a Cloud Architect, you'll need to follow a structured path.
Educational Background and Certifications
- Bachelor's Degree: Typically in computer science or a related field.
- Certifications: Earning certifications from cloud service providers, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect or Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect, is highly beneficial.
Gaining Practical Experience
Hands-on experience is invaluable. Work on cloud projects, participate in internships, or secure junior cloud roles to build your expertise.
Building a Strong Portfolio
Creating a portfolio of your cloud projects and achievements can help you stand out to potential employers.
Challenges and Trends
The field of cloud architecture is not without its challenges. Security, data privacy, and compliance remain ongoing concerns. Additionally, the cloud architecture landscape continually evolves. Emerging trends include serverless computing, multi-cloud strategies, and edge computing.
Conclusion
As technology becomes increasingly reliant on the cloud, the role of a Cloud Architect becomes ever more critical. Their expertise in designing, implementing, and maintaining cloud solutions is the linchpin of a successful cloud strategy.
The demand for Cloud Architects is expected to grow, making it a promising career choice. However, staying updated with the latest trends and continuously honing your skills is crucial in this dynamic field.
For more insights into the world of cloud architecture and how to become a Cloud Architect, explore our articles and resources.
FAQs
- What is the role of a Cloud Architect?A Cloud Architect is responsible for designing and overseeing an organization's cloud infrastructure to ensure optimal performance and security.
- How do I become a Cloud Architect?To become a Cloud Architect, you typically need a relevant degree, certifications from cloud service providers, practical experience, and a strong portfolio.
- What are the major cloud service providers?Major cloud service providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- What are the current challenges in cloud architecture?Current challenges in cloud architecture include data security, compliance, and privacy concerns.
- What are the emerging trends in cloud architecture?Emerging trends in cloud architecture include serverless computing, multi-cloud strategies, and edge computing.




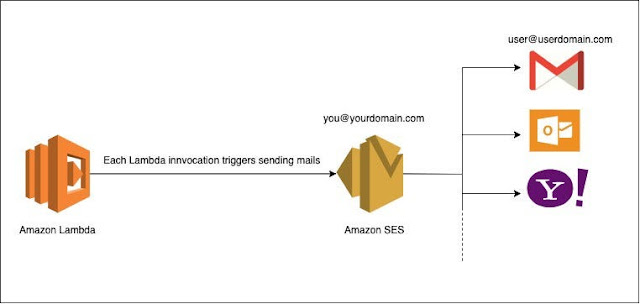

.png)


Comments
Post a Comment